Calculating distant shading
To assess the shading impact on a dwelling, you will need to input key details about surrounding obstacles that may block sunlight.
Required Inputs:
- Shading Direction: Define the start and end angles (in degrees) where the shading occurs, measured from north (0°).
- Obstacle Height: Enter the height (in meters) of the object causing the shading.
- Obstacle Distance: Provide the distance (in meters) from the dwelling to the shading object.
These inputs will help determine how much sunlight is blocked at different times of the day and year, which is crucial for energy efficiency and solar access planning.
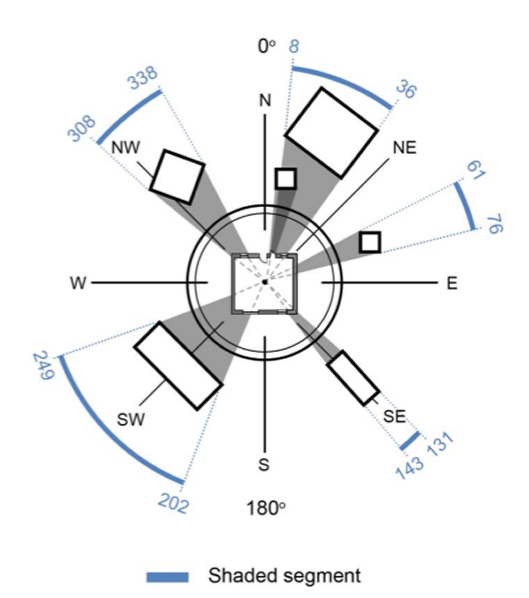
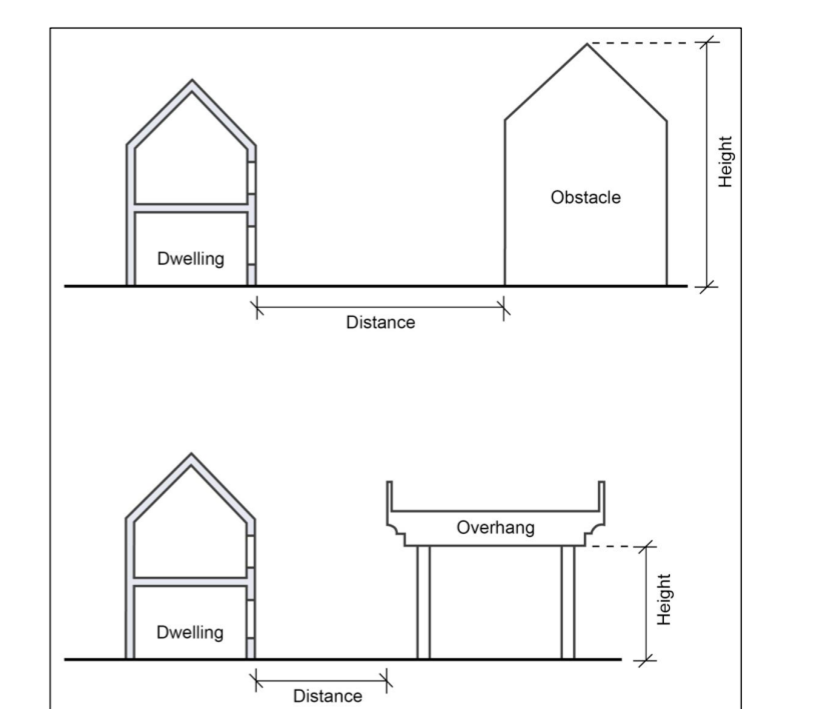
When identifying a shading segment, details of the most significant shading object in that direction should be recorded. This includes:
- The height of the object from the ground.
- The distance from the centre of the closest external wall of the dwelling to the centre of the nearest face of the shading object.
If the shading object has a varying vertical cross-section, its height will be measured at the midpoint of the object.
The key difference between obstacles and overhangs is:
- An obstacle (e.g., a tree or building) ends at a certain height above ground level.
- An overhang (e.g., a roof or balcony) starts at a certain height above ground level.